Github : https://github.com/bboz/Computational_Geometry
1.Hafta Ders İçeriği
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=[4,0]
y=[0,3]
get_ipython().magic('matplotlib inline')
plt.plot(x,y)
def my_draw_a_vector_from_origin(v):
# from origin to v
plt.axes().set_aspect('equal')
x=[0,v[0]]
y=[0,v[1]]
plt.xlim(-10,15) #sınır değerleri ayarlıyoruz
plt.ylim(-10,15)
plt.plot(x,y)
my_draw_a_vector_from_origin([5,67])
def my_draw_a_vector_from_v_to_w(v,w):
# from origin to v
x=[v[0],w[0]]
y=[v[1],w[1]]
plt.xlim(-10,15) #sınır değerleri ayarlıyoruz
plt.ylim(-10,15) #sınır değerleri ayarlıyoruz
plt.plot(x,y)
my_draw_a_vector_from_v_to_w([5,6],[5,20])
#vektorun bir baska vektor ile skaler carpimi yapıcak
def my_scalar_product(a,b):
return (a[0]*b[0]+a[1]*b[1])
v=[3,4]
w=[4,7]
my_scalar_product(v,w)
#dik durumda iki vektor carpinca sifir gelmeli
v=[0,4]
w=[3,0]
my_scalar_product(v,w)
my_draw_a_vector_from_origin(v)
my_draw_a_vector_from_origin(w)
my_scalar_product(v,w)
my_draw_a_vector_from_v_to_w([5,5],[10,12])
my_draw_a_vector_from_origin([-7,5])
my_draw_a_vector_from_origin([4,3])
my_draw_a_vector_from_origin([-3,4])
my_scalar_product([4,3],[-3,4])
def distance(v,w):
return (((v[0]-w[0])**2) + ((v[1]-w[1])**2))**.5
def my_vector_add(v,w):
return [v[0]+w[0],v[1]+w[1]]
def my_vector_substract(v,w):
return [v[0]-w[0],v[1]-w[1]]
def my_vector_multiply_with_scalar(c,v):
return [c*v[0],c*v[1]]
a=[3,0]
b=[0,4]
print("toplam : ",my_vector_add(a,b))
print("fark : ",my_vector_substract(a,b))
print("5 kati : ",my_vector_multiply_with_scalar(5,b))
print("uzunluk :",distance(a,b))
 |
| my_draw_a_vector_from_origin([5,67]) |
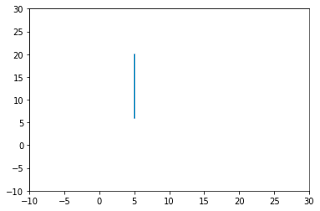 |
| my_draw_a_vector_from_v_to_w([5,6],[5,20]) |
2.Hafta Ders İçeriği
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
point1=np.array([0,0,0])
#orjinden geçen x=1 y=-2 z=1 olan bir normal var meshgrid yapısı ile oluşturucaz point-nokta normal-doğru
normal1=np.array([1,-2,1])
point2=np.array([0,-4,0])
normal2=np.array([0,2,-8])
point3=np.array([0,0,1])
normal3=np.array([-4,5,9])
point_test = np.array([1,-1,1])
#np bu listeleri çarpabiliyor , kullanmadan yaparsak hata alırız
normal_test = np.array([1,-2,1])
np.sum(point_test*normal_test)
d1 = -np.sum(point1*normal1) # dot product -- distance
d2 = -np.sum(point2*normal2) # dot product -- distance
d3 = -np.sum(point3*normal3) # dot product -- distance
d1,d2,d3
# 4x+5y+6z+7 -<4>. = d skaler çarpma aradaki işlem
xx,yy=np.meshgrid(range(5),range(5))
xx # 5^3 değeri 125 tane değer geliyor 3 boyutlu
yy
z1 = (-normal1[0]*xx - normal1[1]*yy - d1)*1./normal1[2]
get_ipython().magic('matplotlib inline')
plt3d = plt.figure().gca(projection='3d')
plt3d.plot_surface(xx,yy,z1,color='blue')
# ax+by+cz+d=0 bir doğruysa şu şekilde çevirebiliyoruz z=(-d-ax-by)/c
point_test = np.array([1,-1,1])
#np bu listeleri çarpabiliyor , kullanmadan yaparsak hata alırız
normal_test = np.array([1,-2,1])
np.sum(point_test*normal_test)
d1 = -np.sum(point1*normal1) # dot product -- distance
d2 = -np.sum(point2*normal2) # dot product -- distance
d3 = -np.sum(point3*normal3) # dot product -- distance
d1,d2,d3
# 4x+5y+6z+7 -<4>. = d skaler çarpma aradaki işlem
xx,yy=np.meshgrid(range(5),range(5))
xx # 5^3 değeri 125 tane değer geliyor 3 boyutlu
yy
z1 = (-normal1[0]*xx - normal1[1]*yy - d1)*1./normal1[2]
get_ipython().magic('matplotlib inline')
plt3d = plt.figure().gca(projection='3d')
plt3d.plot_surface(xx,yy,z1,color='blue')
# ax+by+cz+d=0 bir doğruysa şu şekilde çevirebiliyoruz z=(-d-ax-by)/c
# deniyelim çizdirelim
n = 1000
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# Plot a helix along the x-axis
theta_max = 8 * np.pi
theta = np.linspace(0, theta_max, n)
x = theta
z = np.sin(theta)
y = np.cos(theta)
ax.plot(x, y, z, 'b', lw=2)
# An line through the centre of the helix
ax.plot((-theta_max*0.2, theta_max * 1.2), (0,0), (0,0), color='k', lw=2)
# sin/cos components of the helix (e.g. electric and magnetic field
# components of a circularly-polarized electromagnetic wave
ax.plot(x, y, 0, color='r', lw=1, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot(x, [0]*n, z, color='m', lw=1, alpha=0.5)
# Remove axis planes, ticks and labels
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show()
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
n=1000
thete_max=0*np.pi
theta=np.linspace(0,theta_max,n)
x=np.sin(theta) #theta
y=np.cos(theta)
z=theta
ax.plot(x,y,z,'b',lw=2)
3.Hafta Ders İçeriği
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
def draw_my_line(normal_vector,point_on_line):
a=normal_vector[0]
b=normal_vector[1]
c=normal_vector[2]
x_0=point_on_line[0]
y_0=point_on_line[1]
z_0=point_on_line[2]
x=[]
y=[]
z=[]
#x.append(other_point[0])
#y.append(other_point[1])
#z.append(other_point[2])
for t in range(-100,100):
x.append(x_0+t*a)
y.append(y_0+t*b)
z.append(z_0+t*c)
return (x,y,z)
def my_scalar_product(a,b):
#a=[-1,-2,4]
#b=[-2,-5,2]
# a tanspose b ?
a_t_b=a[0]*b[0]+a[1]*b[1]+a[2]*b[2]
return a_t_b
def point_on_line(normal_vector,point_on_line,other_point):
a_x=other_point[0]-point_on_line[0] # otherpoint pointOnLine ikilisi
a_y=other_point[1]-point_on_line[1]
a_z=other_point[2]-point_on_line[2]
b=[a_x,a_y,a_z]
a=normal_vector
c=my_scalar_product(a,b)/my_scalar_product(a,a)
b_x=c*a[0]
b_y=c*a[1]
b_z=c*a[2]
nearest_point_on_line=(b_x,b_y,b_z)
return nearest_point_on_line
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'notebook')
p=(0,0,0)
n=(1,1,1) #hat üzerinde bir nokta
other_point=[1,1,100]
#bulundugun nokta bekleme noktası
n_p=point_on_line(n,p,other_point)
#neraest point , n_p değeri hat üzerindeki bize en yakın nokta
points=draw_my_line(n,p)
ax=plt.axes(projection='3d')
#ax.plot3D(points[0],points[1],points[2],'red')
#ax.plot3D(3,4,5,'red')
ax.plot3D(points[0],points[1],points[2],'red')
ax.scatter(other_point[0],other_point[1],other_point[2],'*')
ax.scatter(n_p[0],n_p[1],n_p[2],'*')
plt.show()
4.Hafta Ders İçeriği
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
def my_product(a,b):
return a[0]*b[0]+a[1]*b[1]+a[2]*b[2]
def my_length_function(a): #gelen vektörün uzunluğunu vericek
return my_product(a,a)**0.5
#düzlemin denklemi ve düzlem üzerindeki noktayı gondericez fonksiyona
def plane_point(plane,point):
plane_normal=[plane[0],plane[1],plane[2]]
d=my_product(plane_normal,point) / my_length_function(plane_normal)
t=(my_product(plane_normal,point))
t=t/my_product(plane_normal,plane_normal)
p_0=[0,0,0]
p_0[0]=point[0]+t*plane[0]
p_0[1]=point[1]+t*plane[1]
p_0[2]=point[2]+t*plane[2]
return d,t,p_0
def plot_planes_lines_points(plane,line_with_two_points,two_points):
plane_normal=[plane[0],plane[1],plane[2]]
d=plane[3]
xx,yy = np.meshgrid(range(-10,20),range(-10,20))
z = (-plane_normal[0] * xx -plane_normal[1] * yy - d)* 1./ plane_normal[2]
plt3d=plt.figure().gca(projection='3d')
plt3d.plot_surface(xx,yy,z,color='red')
point_1=line_with_two_points[0]
point_2=line_with_two_points[1]
points_x=[point_1[0],point_2[0]]
points_y=[point_1[1],point_2[1]]
points_z=[point_1[2],point_2[2]]
plt3d.plot3D(points_x, points_y, points_z)
point_1=two_points[0]
point_2=two_points[1]
points_x=[point_1[0],point_2[0]]
points_y=[point_1[1],point_2[1]]
points_z=[point_1[2],point_2[2]]
plt3d.scatter3D(points_x, points_y, points_z)
plt.show()
%matplotlib notebook
def test():
plane_1=[1,2,3,-6]
point_1=[4,2,10]
#results = plane_point(plane_1,point_1)[2] # 38/kok14 verdi bu bize defterde var
#plane_1=[3,2,6,-6]
#point_1=[1,1,3]
(d,t,p)=plane_point(plane_1,point_1)
plot_planes_lines_points(plane_1,[point_1, p],[point_1, p])
print(d,t,p)
test()
5.Hafta Ders İçeriği
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import math
get_ipython().magic('matplotlib notebook')
n = 1000
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
#plot a helix along the x-axis
theta_max = 8 * np.pi
theta = np.linspace(0, theta_max, n) # 0 dan 8pi ye kadar n tane nokat oluştur
x = np.sin(theta)
y = np.cos(theta)
z = theta
ax.plot(x, y, z, 'b', lw=2)
#ax.set_axis_off()
theta_current = 3 * np.pi/2
#türevini aldık çalıştığımız nokta 3*np.pi/2 olsun dedik ordaki türev x_1,y_1,z_1 vektörü
x_1=math.cos(theta_current)
#bunlar ordaki teğet olan vektörün büyüklüğü
y_1=math.sin(theta_current)
z_1=1
x_2=math.sin(theta_current)
y_2=-math.cos(theta_current)
z_2=theta_current
x_3=x_1+x_2
y_3=y_1+y_2
z_3=z_1+z_2
x_s=[x_3,x_2]
y_s=[y_3,y_2]
z_s=[z_3,z_2]
ax.plot(x_s,y_s,z_s) # iki nokta var birleştiriceğiz
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import math
get_ipython().magic('matplotlib notebook')
n = 1000
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
#plot a helix along the x-axis
theta_max = 8 * np.pi
theta = np.linspace(0, theta_max, n) # 0 dan 8pi ye kadar n tane nokat oluştur
a=5
b=7
x = a*np.sin(theta)
y = b*np.cos(theta)
z = theta
ax.plot(x, y, z, 'b', lw=2)
#ax.set_axis_off()
theta_current = 3 * np.pi/2
#türevini aldık çalıştığımız nokta 3*np.pi/2 olsun dedik ordaki türev x_1,y_1,z_1 vektörü
x_1=math.cos(theta_current)
#bunlar ordaki teğet olan vektörün büyüklüğü
y_1=math.sin(theta_current)
z_1=1
x_2=a*math.sin(theta_current)
y_2=b*-math.cos(theta_current)
z_2=theta_current
x_3=x_1+x_2
y_3=y_1+y_2
z_3=z_1+z_2
x_s=[x_3,x_2]
y_s=[y_3,y_2]
z_s=[z_3,z_2]
ax.plot(x_s,y_s,z_s) # iki nokta var birleştiriceğiz
plt.show()
8.Hafta Ders İçeriği
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
#%matplotlib notebook
fig=plt.figure()
ax=Axes3D(fig)
X=np.arange(-14,14,0.25)
Y=np.arange(-14,14,0.25)
X, Y=np.meshgrid(X,Y)
#R=np.sqrt(X**2+Y**2)
R=(X**2+Y**2)
Z=np.sin(R)
Z_planes=-5+2*X+4*Y
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, R, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='hot')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z_planes, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='hot')




Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder